Paternity testing is one of the most precise ways to confirm biological relationships, and it’s a topic that touches legal, medical, and emotional worlds alike. Whether used to establish child support, verify family ties in immigration cases, or bring personal peace of mind, DNA paternity testing provides scientifically grounded answers when they matter most.
A DNA paternity test compares specific genetic markers in a child’s DNA to those of an alleged father to determine biological parentage. These tests can be completed at home for personal clarity or through accredited laboratories when legal verification is required.
This guide breaks down what employers, HR leaders, and individuals need to know about the paternity testing process, reasons for testing, types of tests, accuracy rates, and the human side of receiving results.
Learn how DNA testing works, how reliable results are, and what steps ensure tests meet legal and scientific standards.
What Is a DNA Paternity Test?
A paternity test compares the child’s genetic profile to that of the alleged father. Analysts focus on short tandem repeat (STR) markers — segments of DNA that vary between individuals — to determine whether the tested man’s profile matches the child’s.
Unlike other genetic tests that identify inherited health risks or ancestry, DNA paternity testing serves a single purpose: confirming or excluding biological parentage.
When conducted through an accredited laboratory, DNA paternity test results are remarkably accurate. Tests confirm inclusion with more than 99.99% accuracy and exclude non-fathers with 100% certainty, though a small margin for error exists due to rare genetic mutations or sample mishandling.
Why Do People Get Paternity Tests?
The motivations behind paternity DNA testing vary widely. While most associate it with family or custody disputes, there are multiple legal, medical, and personal reasons for confirming a biological relationship.
Legal Reasons
In the context of family law, paternity testing often becomes essential. Courts may order a legal DNA test to resolve disputes around child support, child custody, or inheritance rights. Employers who work with court-ordered or family-related leave cases — such as under the Family and Medical Leave Act — may also encounter documentation related to these results, making awareness of legal DNA testing standards useful.
Immigration
DNA tests are frequently used to establish biological relationships in immigration and citizenship applications, especially when paper documentation is unavailable or inconclusive. The U.S. Department of State accepts only Association for the Advancement of Blood & Biotherapies (AABB) accredited test results for immigration purposes.
Medical History
Determining paternity can fill critical gaps in a person’s medical history. Knowing a child’s biological lineage allows healthcare providers to identify hereditary diseases, assess genetic risk factors, and ensure accurate records for future care.
Personal Reasons
Some families seek paternity testing privately to resolve lingering doubts or to confirm family connections before pursuing legal steps. While this can be an emotionally sensitive process, it can also bring relief and closure once results are known.
When Is a DNA Paternity Test Performed?
The timing of a DNA paternity test depends on individual circumstances and legal requirements. Tests may occur before birth, immediately after birth, or later in life, depending on the need for verification.
Prenatal Paternity Testing
Prenatal paternity testing can determine biological relationships before a child is born. The most common method involves analyzing fetal DNA found in the mother’s bloodstream as early as seven weeks into pregnancy. This non-invasive test poses no risk to the baby. In more complex cases, invasive methods like amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling may be used, though they carry minor medical risks.
Post-Birth Testing
The most common form of paternity DNA testing occurs after a child is born. A painless cheek swab is collected from both the child and the alleged father. In some cases, the mother’s sample is also included to strengthen the accuracy of the result.
Court-Ordered or Voluntary Testing
Legal cases involving custody, child support, or adoption often require a court-ordered paternity test to establish parentage. These tests follow strict chain-of-custody procedures and are admissible in court. Voluntary testing, on the other hand, may be used when all parties agree to establish paternity without court involvement.
Time-Sensitive Situations
Sometimes paternity must be confirmed quickly, such as in immigration filings, insurance claims, or medical decision-making. In those situations, expedited processing options are available through professional testing providers.
How Do DNA Paternity Tests Work?
Every DNA paternity test follows a scientific, step-by-step process that ensures accuracy and reliability:
- Sample collection: A painless buccal (cheek) swab collects epithelial cells from the inside of the mouth. This method is non-invasive, fast, and yields high-quality DNA samples.
- DNA extraction: The laboratory isolates genetic material from the collected cells for analysis.
- Marker comparison: Technicians compare 15–20 STR genetic markers shared between the child and the alleged father.
- Statistical analysis: Advanced software calculates the probability of paternity. A 99.99% or greater probability confirms paternity; a 0% probability excludes it.
- Result reporting: The laboratory provides a written test result summarizing the findings, including the paternity index and conclusion.
In rare instances, factors like sample contamination, mislabeling, or genetic mutations can complicate interpretation. Accredited labs, such as those certified by AABB, have safeguards in place to minimize such risks, ensuring a reliable result every time.
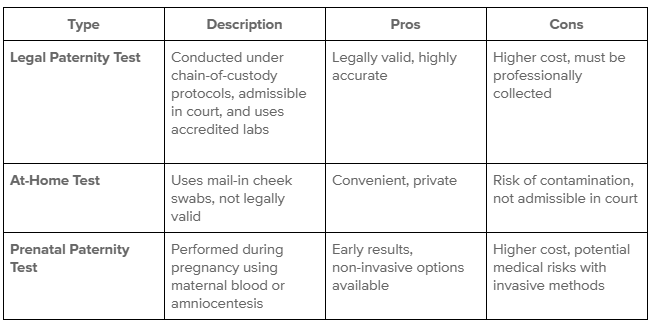
Types of Paternity Tests
Paternity testing methods vary based on the purpose and legal requirements.
How Reliable Are DNA Paternity Test Results?
So, how reliable are DNA paternity tests? The short answer is exceptionally reliable when performed correctly.
Modern DNA paternity testing uses advanced genetic sequencing to compare dozens of STR markers. When samples are collected and processed in an accredited lab, the accuracy exceeds 99.99% for confirmed paternity and is 100% accurate in excluding a non-father.
However, several factors can influence reliability:
- Sample handling: Home tests can be less dependable if the swabs are contaminated or mislabeled.
- Chain of custody: Legal DNA tests must adhere to strict identification and documentation procedures to ensure validity.
- Genetic mutations: Although rare, small mutations can appear in the child’s DNA that don’t perfectly match the father’s. Skilled analysts account for these during result interpretation.
- Number of markers tested: Accredited labs test more genetic markers than consumer kits, reducing the chance of ambiguous results.
Ultimately, while a home paternity test can provide peace of mind, only a legal DNA test conducted under chain-of-custody standards can be used for court cases, child support orders, or immigration petitions.
The Risks and Common Misconceptions of Paternity Testing
Despite scientific rigor, paternity testing is surrounded by misconceptions that can cause confusion or emotional distress.
Emotional Risks
Learning the results of a paternity DNA test can impact family relationships and emotional well-being. It can create relief for some and shock or sadness for others, particularly when results contradict long-held assumptions. Employers managing workplace leave or counseling benefits may encounter employees navigating these complex emotions.
Misconceptions About Accuracy
Many assume that at-home DNA tests are just as accurate as legal tests, but without professional oversight, results may not meet court standards. Another common myth is that only the father’s DNA is needed. Including the mother’s sample can actually improve accuracy and clarify borderline results.
Legal Misconceptions
Some believe they can use an at-home test in child custody or child support cases, but courts require tests that document a verified chain of custody. Using a home kit for legal purposes can result in delays, added costs, or rejected evidence.
Privacy Concerns
Accredited labs protect all identifying information, while some low-cost online options may not guarantee confidentiality. Choosing a reputable testing provider safeguards personal data and maintains result integrity.
Paternity Testing Costs and Timelines
The cost of a paternity DNA test depends on its type, purpose, and the speed of results required.
- Legal DNA tests: Usually range from $300 to $500 and follow strict documentation requirements, with results typically ready within two to seven business days
- At-home paternity tests: More affordable at $80 to $150, though they lack legal validity, with results returned within three to five business days
- Prenatal paternity tests: Can range from $900 to $2,000, depending on whether non-invasive or invasive collection is used
- Expedited testing: Available for additional fees, with same-week or next-day reporting options
Turnaround times for paternity test results vary by laboratory workload and shipping times, but accredited labs prioritize fast, accurate delivery. Employers or legal representatives handling family verification cases can expect standardized reporting formats suitable for court or HR documentation.
The Emotional Side of Paternity Testing
While the science behind paternity testing is straightforward, the emotions surrounding it are not. Awaiting results can cause stress, anxiety, and uncertainty. When results arrive, reactions may include relief, validation, disappointment, or confusion.
Families often benefit from open communication throughout the testing process. Counselors, family law professionals, or trusted advisors can help navigate sensitive conversations, especially when children are involved. In some cases, receiving clear results helps rebuild trust and stability within families by ending uncertainty.
For employers, recognizing that employees may be experiencing personal or family-related stress following DNA test results can guide compassionate management responses and resource referrals.
Trust Fastest Labs for Accurate and Reliable DNA Paternity Testing
DNA paternity testing delivers accurate answers when accuracy matters most. To ensure dependable results, always choose an accredited laboratory that maintains strict chain-of-custody standards and clear documentation.
Fastest Labs offers professional legal DNA testing and efficient collection procedures that support both personal and court-required cases. Our certified collectors deliver fast, accurate results and complete confidentiality.
Take the first step toward clarity and confidence by finding a Fastest Labs near you.



.0000000000000.jpg)